
Chandrayan 3 – Cameras!
Aug 24 2023
Space program is interesting Phenomenon invented by Mankind, Cameras play very much important role during the space exploration to document.
Nasa has used many cameras on the space craft in the past…recently it had an agreement with Red Digital Cinema camera for filming the lives of the scientists through the Space Journey Red Helium 8k was used.
Earlier it had
- Apollo TV camera
- Hasselblad “Electric Camera” (modified 500 EL) with 70 mm film
- Maurer Data Acquisition Camera (DAC) with 16 mm film
- Nikon F with 35 mm film
- Stellar Camera (7.6 cm focal length) with 35 mm film, on Apollo 15, 16, and 17
- Panoramic Camera (61 cm focal length) with 127 mm film, on Apollo 15, 16, and 17
Imax cameras with 1000 feet magazines where also used.
Coming to Chandrayan 3 which is a great feet achieved by ISRO landing on the South Pole of the Moon.

The Cameras used are
The Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera (LHVC), which is onboard the Vikram, has already clicked the first image of the moon during its descent on the lunar surface on Wednesday.
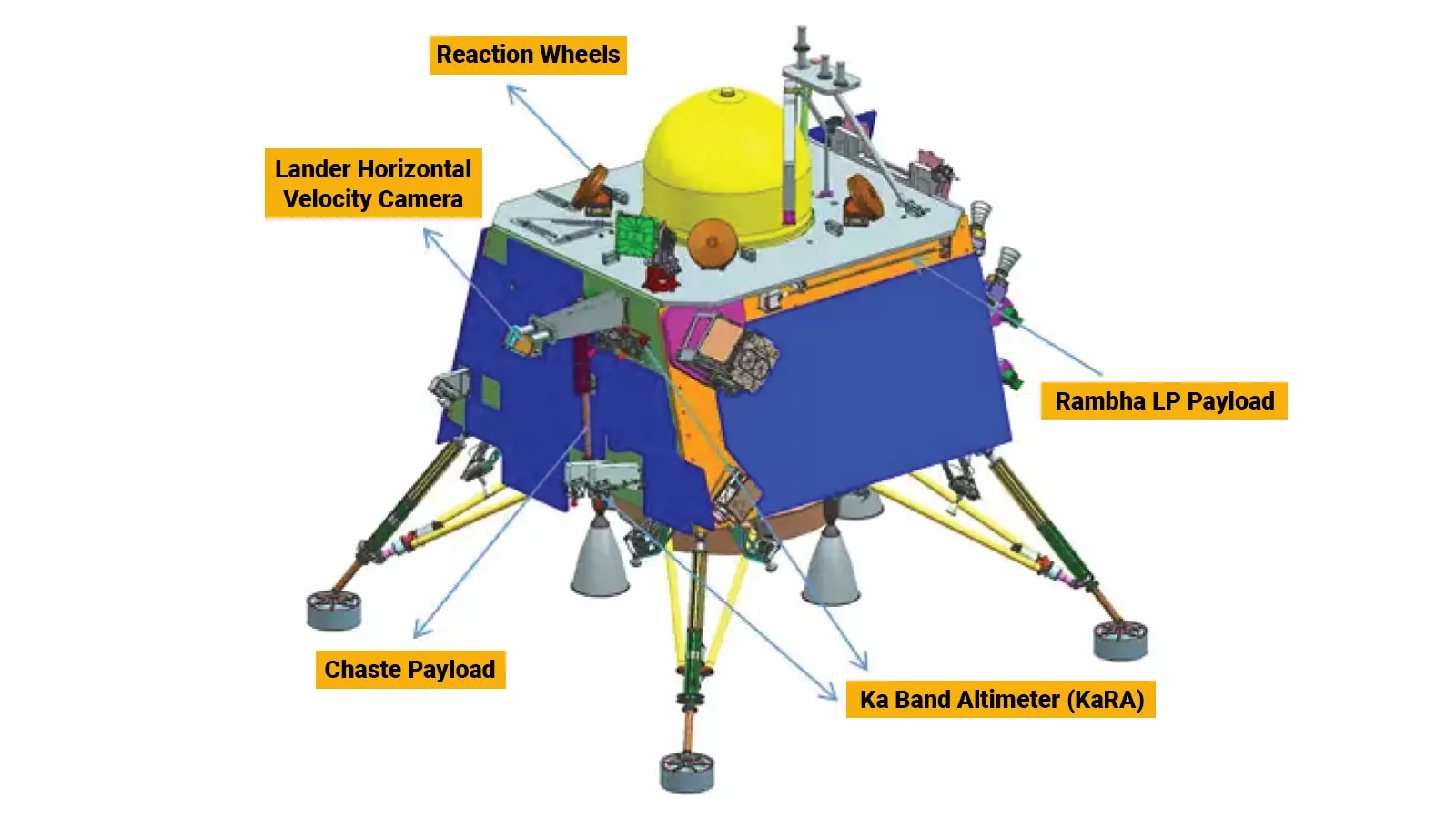
LHVC, which was initially developed for the Chandrayaan-2 mission, has also been adopted for the Chandrayaan-3 mission.
“LHVC has an important role of measuring horizontal velocity during the Lander descent phase. It does a complex algorithm calculating the velocity in which the lander is travelling. This instrument provides important information during the descent,
* OHRC ( orbitor high resolution camera) which is capable of recording light wavelength of (450nm- 800nm) from 25cm to 100km this high resolution camera is an important tool for lunar topographic studies of select regions.
is a very high spatial resolution camera operating in visible panchromatic(PAN) band. OHRC measures the solar light reflected from the lunar surface in visible range of electromagnetic spectrum. This camera is designed for imaging in very low sun elevation conditions. OHRC images were extensively used for landing sites characterization to detect the small-scale features particularly smaller boulders on lunar surface. Ground sampling distance (GSD) and swath of OHRC (in nadir view) are 0.25m and 3km respectively, from a 100 km altitude. OHRC has the capability to produce multiview stereo images by spacecraft maneuvering. These stereo pairs can be used to generate the highest resolution Digital elevation model (DEM) so far available for the Lunar surface. This study provides the
DEM generation capability from OHRC multiview (Stereo) images of few specific areas of moon surface.
* TMC-2 (Terrain mapping camera)
The images captured by the TMC of Chandrayaan-1 mission have been found to be extremely useful as it returned
orbital high resolution stereo images and the unprecedented view of the lunar surface at that time. This
enabled the maiden three-dimensional mapping of a volcanic lava tube on Moon4, which could be used for
habitability of base station in future.
TMC will measure the solar radiation reflected / scattered from Moon surface. The dynamic range of the reflected signal is quite large (>300), represented by the two extreme targets – fresh rock surface and mature mare soil.
Lander Hazard Avoidance camera (LHDAC)
HazCams detect hazards to the front and back pathways of the rover, such as large rocks, trenches, or sand dunes. Engineers also use the front HazCams to see where to move the robotic arm to take measurements, photos, and collect rock and soil samples.
Enhanced Engineering Cameras
The enhanced engineering cameras for driving help human operators on Earth drive the rover more precisely, and better target the movements of the arm, drill and other tools that get close to their targets. A much wider field-of-view gives the cameras a much better view of the rover itself.


It is amazing to see the images from the Lander Horizontal Velocity camera during the descent of the Moon.
Article by
CJ Rajkumar
Author/Cinematographer
